Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Cosmology
Cosmology: Exploring the Origins, Evolution, and Nature of the Universe
Introduction:
Cosmology is a captivating branch of science that seeks to understand the origins, evolution, and fundamental nature of the universe. It explores the vast expanse of space, the distribution of matter and energy, and the forces and laws that govern the cosmos. By studying the universe on its largest scales and employing theoretical models, observational data, and advanced technologies, cosmologists strive to unravel the mysteries of our existence and our place within the cosmos. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of cosmology, exploring its key concepts, advancements, and contributions to our understanding of the universe.
The Big Bang Theory and the Early Universe:
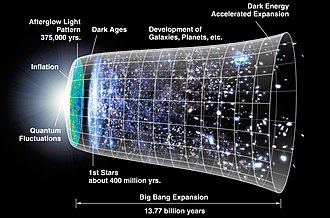
The Big Bang theory forms the foundation of modern cosmology. It proposes that the universe originated from a hot, dense state approximately 13.8 billion years ago. According to this theory, the universe has been expanding and evolving ever since, giving rise to the vast structures we observe today.
The early universe, shortly after the Big Bang, was a seething sea of high-energy particles. As the universe expanded and cooled, elementary particles formed, eventually combining to form atoms. The cosmic microwave background radiation, discovered in 1964, provides a snapshot of this early era and serves as crucial evidence for the Big Bang theory.
Inflationary Cosmology:
Inflationary cosmology is a concept that postulates a period of exponential expansion in the early universe, immediately following the Big Bang. This rapid expansion helps explain the observed uniformity and structure of the cosmos on large scales. Inflationary models suggest that tiny quantum fluctuations during this inflationary phase gave rise to the density variations that eventually led to the formation of galaxies and other cosmic structures.
The Large-Scale Structure of the Universe:
Cosmology investigates the large-scale structure of the universe, including the distribution of galaxies, clusters of galaxies, and cosmic voids. Through surveys and observations, cosmologists have constructed maps that reveal the filamentary structure of the cosmic web—a vast network of interconnected structures.
Dark Matter and Dark Energy:
One of the greatest mysteries in cosmology is the nature of dark matter and dark energy. Dark matter is an invisible form of matter that does not interact with light or other electromagnetic radiation but exerts gravitational effects. It constitutes a significant portion of the total matter in the universe and plays a crucial role in the formation and evolution of cosmic structures.
Dark energy, on the other hand, is an enigmatic form of energy that permeates space and is responsible for the accelerated expansion of the universe. Its nature remains largely unknown, but its existence is supported by observational evidence.
The Fate and Future of the Universe:
Cosmologists explore the fate and future of the universe by studying its expansion rate and the balance between gravitational attraction and dark energy's repulsive effects. Depending on the amount of matter and dark energy in the universe, various scenarios have been proposed, including the possibilities of a Big Freeze, Big Crunch, or even a Big Rip.
Multiverse and Quantum Cosmology:
Cosmology also touches upon concepts beyond our observable universe. The multiverse theory suggests the existence of multiple universes, each with its own set of physical laws and conditions. This idea emerges from theories such as string theory and inflationary cosmology.
Quantum cosmology explores the application of quantum mechanics to the entire universe. It aims to understand the fundamental nature of space, time, and the universe itself at the smallest scales, where classical notions of time and causality break down.
Conclusion:
Cosmology represents a captivating journey into the depths of the universe, seeking to unravel its origins, evolution, and fundamental nature. From the explosive beginnings of the Big Bang to the formation of galaxies, the distribution of matter and energy,
and the enigmatic dark matter and dark energy, cosmology provides a framework for understanding the vast cosmos we inhabit. As advancements in technology, observations, and theoretical models continue, cosmology will undoubtedly uncover new mysteries, challenge existing theories, and inspire future generations to explore the profound questions about our place in the universe.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular Posts
Exploration of Moons, Asteroids, and Comets
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment